 |
|
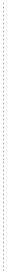 |

|
|
EVALUATION OF EXISTING PAVEMENTS (AIRFIELD)
|
|
>>Back |
GEH’ pavement evaluation and analysis of collected data are effective in rapidly identifying pavement properties and in determining the remaining structural life capacity of a pavement.
|
FUNCTIONAL EVALUATION
GEH performs visual condition surveys, which entail inspecting the pavement surface for both structural and functional distresses and deterioration. Visual condition surveys provide data for both network-level pavement management systems and project-level rehabilitation studies. GEH performs both manual and automated pavement condition surveys, using Pavement Condition Index (PCI) method developed by the US Army Corps of Engineers. GEH uses
U. S. Army Construction
Engineering Research Laboratory (CERL) and
MicroPAVER nomenclature will be utilized for all data input and output.
  
|
|
| |
STRUCTURAL EVALUATION
GEH’s most requested structural evaluation services require testing with
Dynatest Falling Deflectometer (FWD) or the
Heavy Weight Deflectometer (HWD). GEH owns and operates FWD and HWD. The HWD is the preferred device for conducting non-destructive deflection since it has an expanded loading range, simulating up to a heavy aircraft such as the Boeing 747 (one wheel). Further, the HWD can properly introduce anticipated load/deflection measurements on even heavy pavements such as thick airfield pavements. These equipments provide data for:
• Project-level rehabilitation studies
• Network-level structural characterization
• Overlay and reconstruction design
• Load transfer and loss support studies for concrete pavements
• Assessment of structural support of sub-grade and pavement layers during construction
|
|
|
|
For routine analysis purposes, GEH uses
ELMOD5
back-calculation WindowsTM operating systems program developed by for both flexible and rigid pavements. ELMOD is an acronym for
Evaluation of
Layer
Moduli and
Overlay
Design. This software application allows extremely rapid data reduction and analysis of FWD/HWD measurements, calculating the layer E-moduli for a typical drop sequence in one second or less. Seasonally adjusted E-moduli, residual life, and required overlay (if applicable) are also calculated within seconds. The ELMOD5 pavement analysis and evaluation software package of Dynatest has been developed to overcome some of the limitations of current design systems. It avoids the coverage concept by computing the critical design parameter (stress, strain) at all points across the pavement for a given depth and relates this to pavement life. This approach avoids the errors that can result in simplified methods that approximate passes of different aircraft to passes of an “equivalent” design load.
The ACN/PCN system of rating airport pavements is designated by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) as the only approved method for reporting strength. For analysis of airfield pavements, GEH uses a program (WinPCN), which calculates PCN-values in accordance with the ACN/PCN method, as described in the ICAO design manuals. WinPCN is a Windows 95 & 98 based program that uses the data files from Dynatest FWD/HWD equipment to calculate A CN/PCN values based on the methods used by ICAO. The program includes a database of over one hundred and twenty-five aircraft with ICA O ACN values. Additionally the ACN/PCN programme can calculate a PCN value based on aircraft A CN values and sub-grade CBR values as described in FAA Circular 150/5335 -5. The program supports both
ICAO and FAA standards.
|
 |  |
|
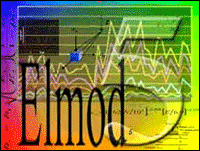
Elmod 5 with WinPCN Module |
|
SAFETY EVALUATION
• Friction Testing
• Roughness Testing
GEH, conducts Safety Evaluation survey, which requires pavement friction testing pavement roughness profile testing. GEH owns and operates K.J. Law Friction Testing equipment and Douglas equipment MK-6 Mu-Meter runway friction measuring and reporting system. The Mu-Meter Mk6 is a continuous friction measuring and reporting system designed for maintenance testing to evaluate surface friction changes due to weathering, high usage, aging, and contaminants such as rubber build-up in the touchdown zones in airfield. MK-6 as runway measurement system, it meets all the FAA and ICAO specifications for friction measuring devices.
|
 |  |
|
|
Mu-Meter MK-6
|
K.J.Law Friction Testing at KKIA
|
|
|
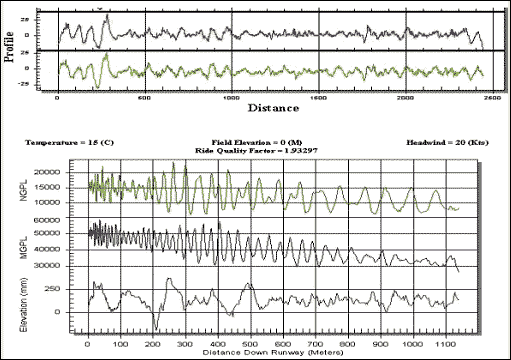
Pavement surface roughness is unevenness or undulations in the pavement surface that results in increased dynamic loading induced into an aircraft structure. Shock loading can result from short wavelength roughness (spalls, step bumps, shoving, etc.). It causes a “shock” to be transmitted through the struts. Passengers and crew feel and report it. A shock at the main gear generally has little influence on the reaction at the nose gear and vice versa.
GEH owns and operates Road Surface Profiler (RSP) Mark II to measure longitudinal deviation that effect aircraft dynamics, ride quality and dynamic loads. The RSP performs continuous, highway-speed measurements of longitudinal and transverse profile, including real-time roughness (IRI and Ride Number), rut depth and texture evaluation, GPS, and geometrics. The primary reason for smooth pavement on airfields is minimization of dynamic response of aircraft. Minimal aircraft dynamic response will reduce dynamic loading on the pavement and will result in longer pavement life. Roughness is an important indicator of pavement comfort and safety issues as follows:
• Discomfort for passengers and pilots
• Fatigue damage to aircraft undercarriages
• Blow tires
• Influences braking distance
• Local premature failure of pavement
|
|

|
|
Roughness Measurment at KKIA, Riyadh
|
 |
|
Roughness Profile
|
|
>>Back |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |



